OCT – EYE CTSCAN
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. With OCT, each of the retina’s distinctive layers can be seen, allowing to map and measure their thickness. These measurements help with diagnosis and provide treatment guidance for glaucoma and retinal diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic eye disease.
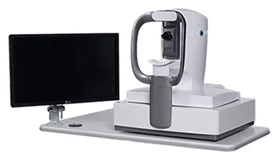
To prepare patient for an optical coherence tomography (OCT) exam, we may put dilating eye drops in patient’s eyes in order to widen their pupil and make it easier to examine the retina.
Patient will be seated in front of the OCT machine and will rest his/her head on a support to keep it motionless. The equipment will then scan his / her eye without touching it.
Scanning takes about 5 to 10 minutes. If the eyes were dilated, patient may be sensitive to light for several hours after the exam.
- Macular hole
- Macular pucker
- Macular edema
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Glaucoma
- Central serous retinopathy
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Preretinal membranes